- Consumer 150
- Posts
- Temu and the Global eCommerce Shockwave:How a Chinese Challenger Redefined Online Retail
Temu and the Global eCommerce Shockwave:How a Chinese Challenger Redefined Online Retail
The rise of Temu marks one of the most striking disruptions in global eCommerce since the emergence of Amazon two decades ago.

Introduction
In less than three years since its international debut in 2022, the Chinese-owned platform—operated by PDD Holdings, the parent company of Pinduoduo—has shaken the foundations of global online retail.
Through a mix of aggressive pricing, social media virality, and data-driven logistics, Temu has redefined consumer expectations around affordability and accessibility. Its explosive growth has also reignited political debates over tariffs, trade imbalances, and supply chain transparency in an era of economic nationalism and shifting global commerce dynamics.
Temu’s ascent occurred against a backdrop of booming eCommerce adoption and heightened geopolitical tensions. The U.S. eCommerce industry itself has grown steadily since 2017, expanding from roughly half a trillion dollars to a projected $1.8 trillion by 2029, representing a compound annual growth rate of 9.2%.
Within that fertile environment, Temu’s timing was near-perfect: an economy eager for discounts, consumers fatigued by inflation, and the proliferation of short-form video marketing all converged to create an opening for a new player. Yet, Temu’s rapid rise has not been without challenges—from regulatory scrutiny and forced labor accusations to the new wave of U.S. tariffs targeting Chinese imports.
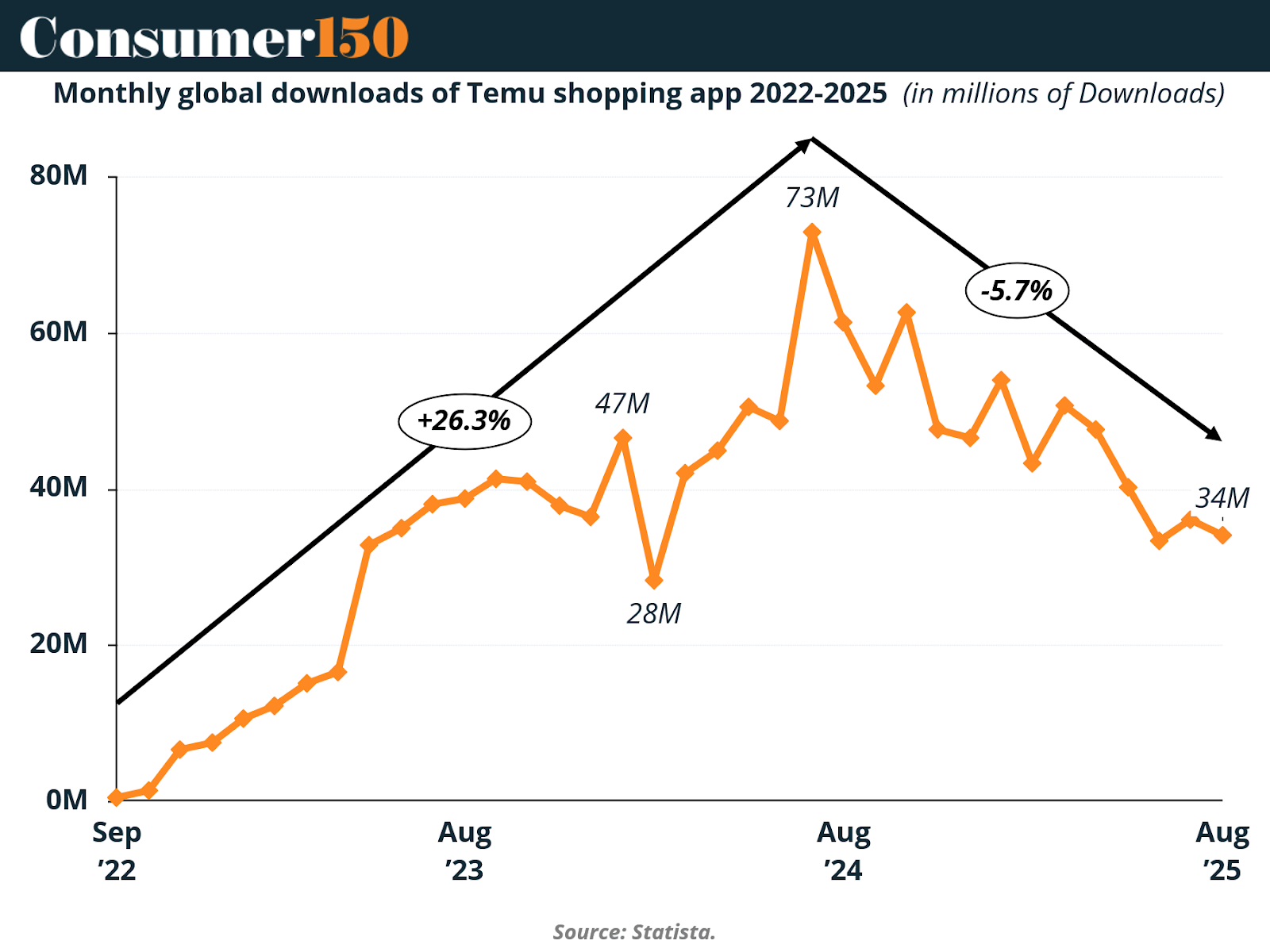
Temu’s global app downloads illustrate both the height of its meteoric rise and the onset of stabilization in a maturing market. From September 2022 to mid-2024, downloads surged by 26%, peaking at 73 million monthly downloads before settling at around 34 million by August 2025—a decline of about 5.7%. This trend suggests that Temu’s initial phase of explosive growth has transitioned into one of consolidation. The decline is less a sign of collapse than an indication that the app has reached a saturation point in its primary markets, particularly in the United States, where growth now hinges on retention and monetization rather than sheer user acquisition.
Temu’s trajectory demonstrates a unique kind of globalization in eCommerce—one propelled not by regional scaling, but by the viral logic of digital ecosystems. The platform’s motto, “Shop like a billionaire,” encapsulates its psychology of abundance, positioning Temu as a platform where anyone can access the world’s manufacturing capacity at near-wholesale prices. But beneath this consumer-friendly narrative lies a complex interplay of data collection, logistics optimization, and aggressive pricing—powered by China’s manufacturing infrastructure and PDD’s unparalleled data analytics system.
Temu Deep Dive
Temu’s parent company, PDD Holdings, is not a new player in the eCommerce landscape. Its Chinese platform Pinduoduo revolutionized domestic retail with its group-buying model, leveraging social engagement to drive down prices and foster viral adoption. When PDD launched Temu for international markets in 2022, it adapted this same formula to Western consumers—combining ultra-low prices, gamified shopping, and fast-paced digital marketing to create a global retail phenomenon.
The numbers behind Temu’s performance are staggering. Despite being a relatively new entrant, Temu has already cracked the list of top global marketplaces by gross merchandise value (GMV), ranking alongside eCommerce titans that have operated for decades.
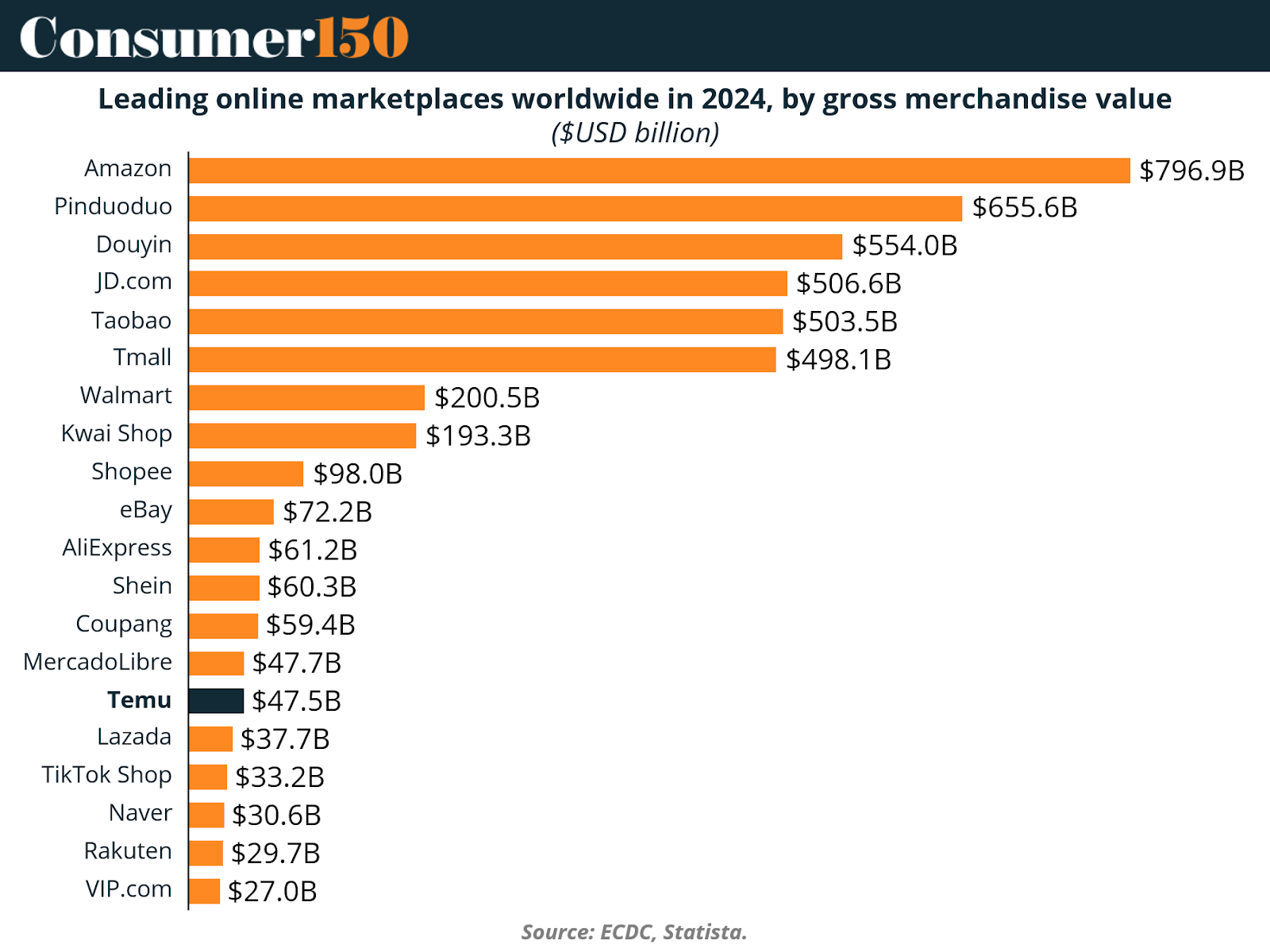
With a GMV of $47.5 billion, Temu sits just behind MercadoLibre and above Lazada, TikTok Shop, and Rakuten. This places it in the company of major incumbents like eBay ($72.2B) and Shopee ($98B), despite Temu’s far shorter operational history. Amazon remains the undisputed leader with $796.9 billion in GMV, but Temu’s presence in the top tier highlights its unparalleled pace of expansion.
PDD’s strategy, however, has not come without cost. The company’s net profit fell in 2025 despite a 7% revenue increase to approximately $14.5 billion in the second quarter. The drop in profitability was attributed to massive investments in marketing, warehousing, and merchant support—mirroring the classic “growth first, profit later” strategy that characterized early Amazon. Executives have openly acknowledged that near-term profit fluctuations are likely, as Temu doubles down on infrastructure to defend market share amid intensifying competition.
In the United States, Temu has been particularly dominant, topping download charts across both major app stores.
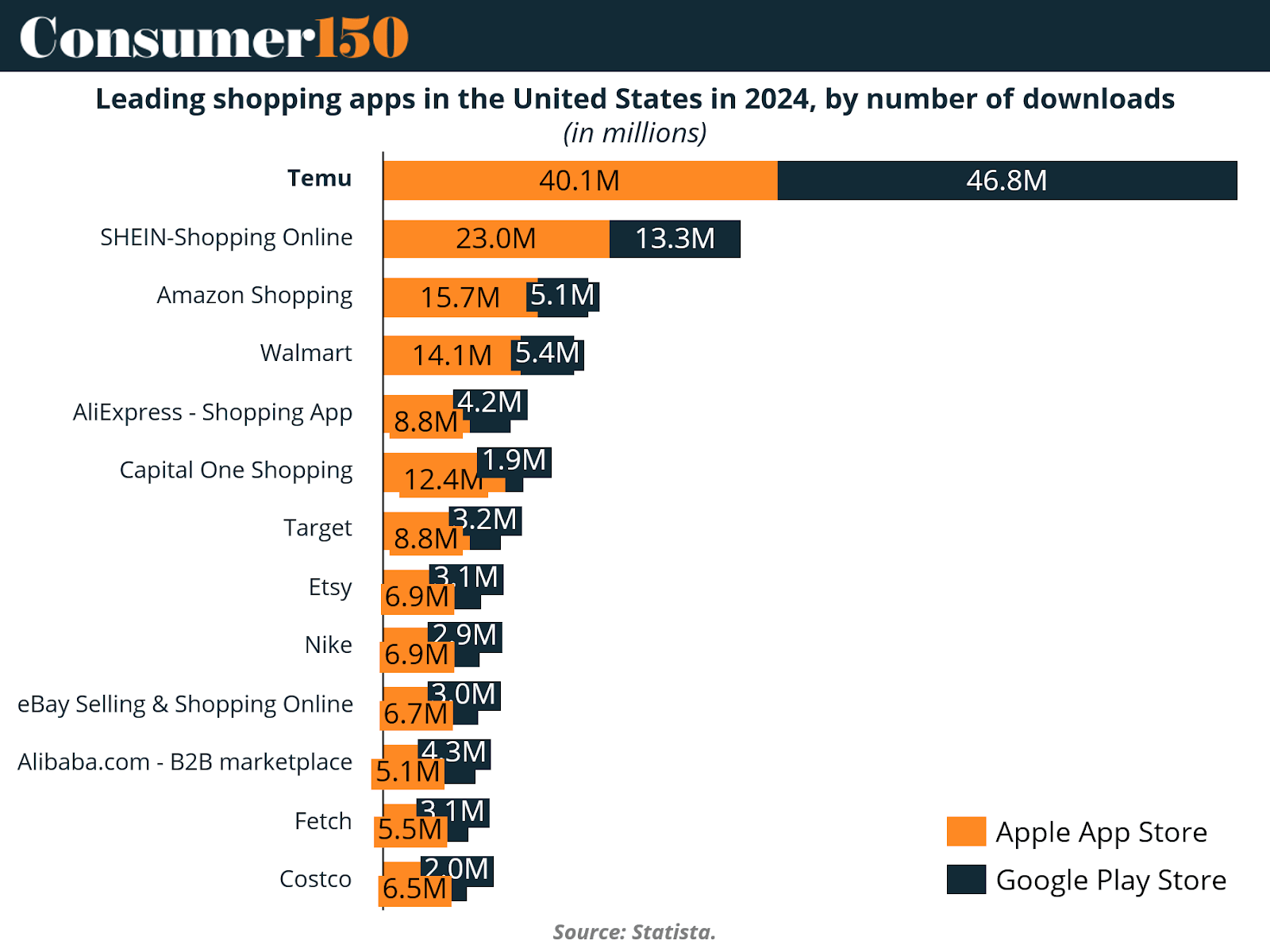
Temu recorded 46.8 million downloads in the U.S. across the Apple App Store and Google Play combined—nearly double the figures of Shein and more than triple Amazon’s. This massive user base reflects Temu’s effective marketing strategy, from high-profile Super Bowl ads to relentless influencer campaigns. The platform’s appeal lies not only in its prices but also in its ability to sustain engagement.
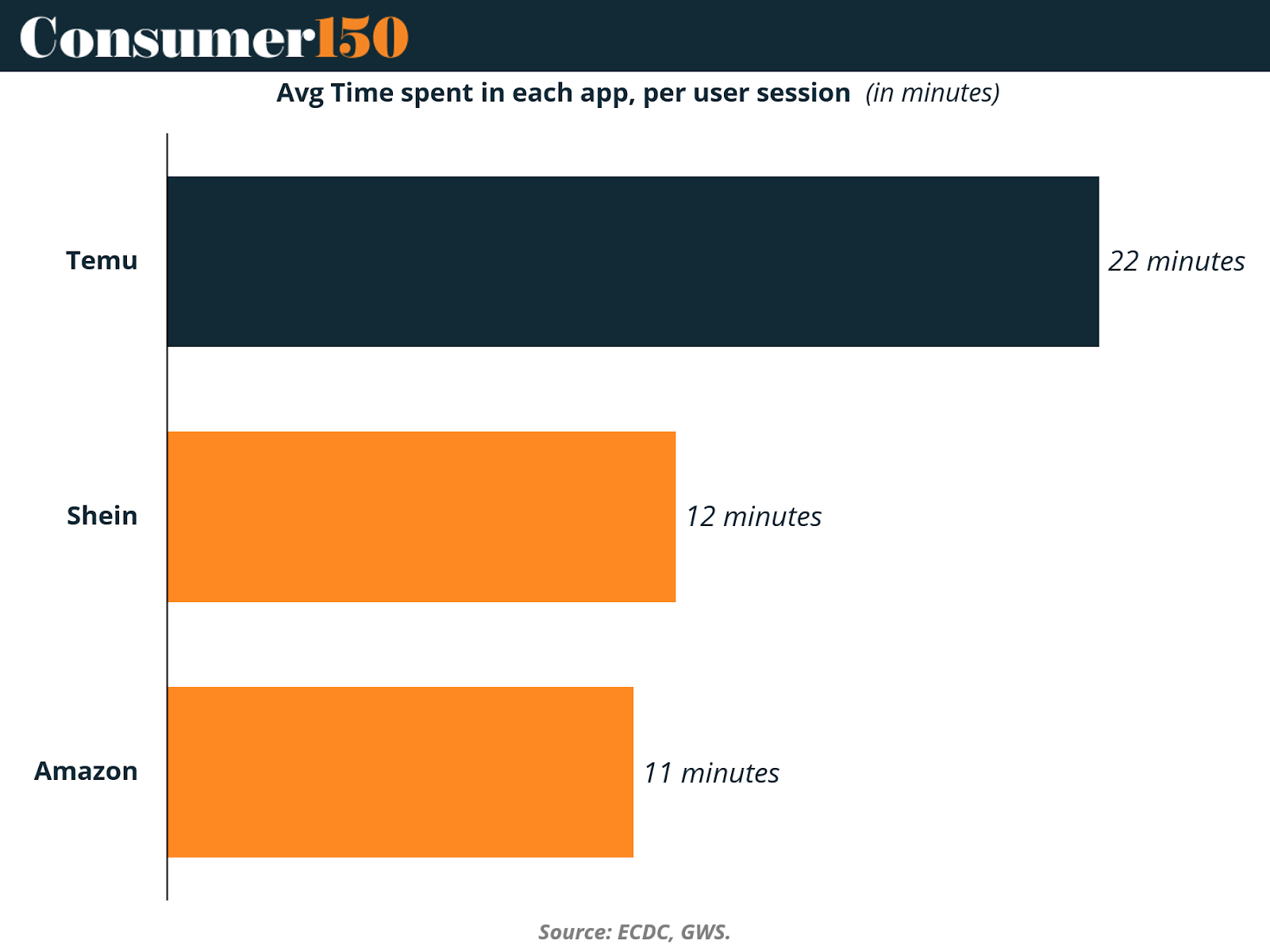
Temu users spend an average of 22 minutes per session, nearly double the engagement time of Shein (12 minutes) and Amazon (11 minutes). This extraordinary retention can be attributed to Temu’s gamified shopping experience—daily check-in bonuses, spin-the-wheel discounts, and interactive referral programs—all designed to keep users within the app longer and increase the likelihood of impulse purchases.
Temu’s traffic metrics tell a similar story of rapid ascent.
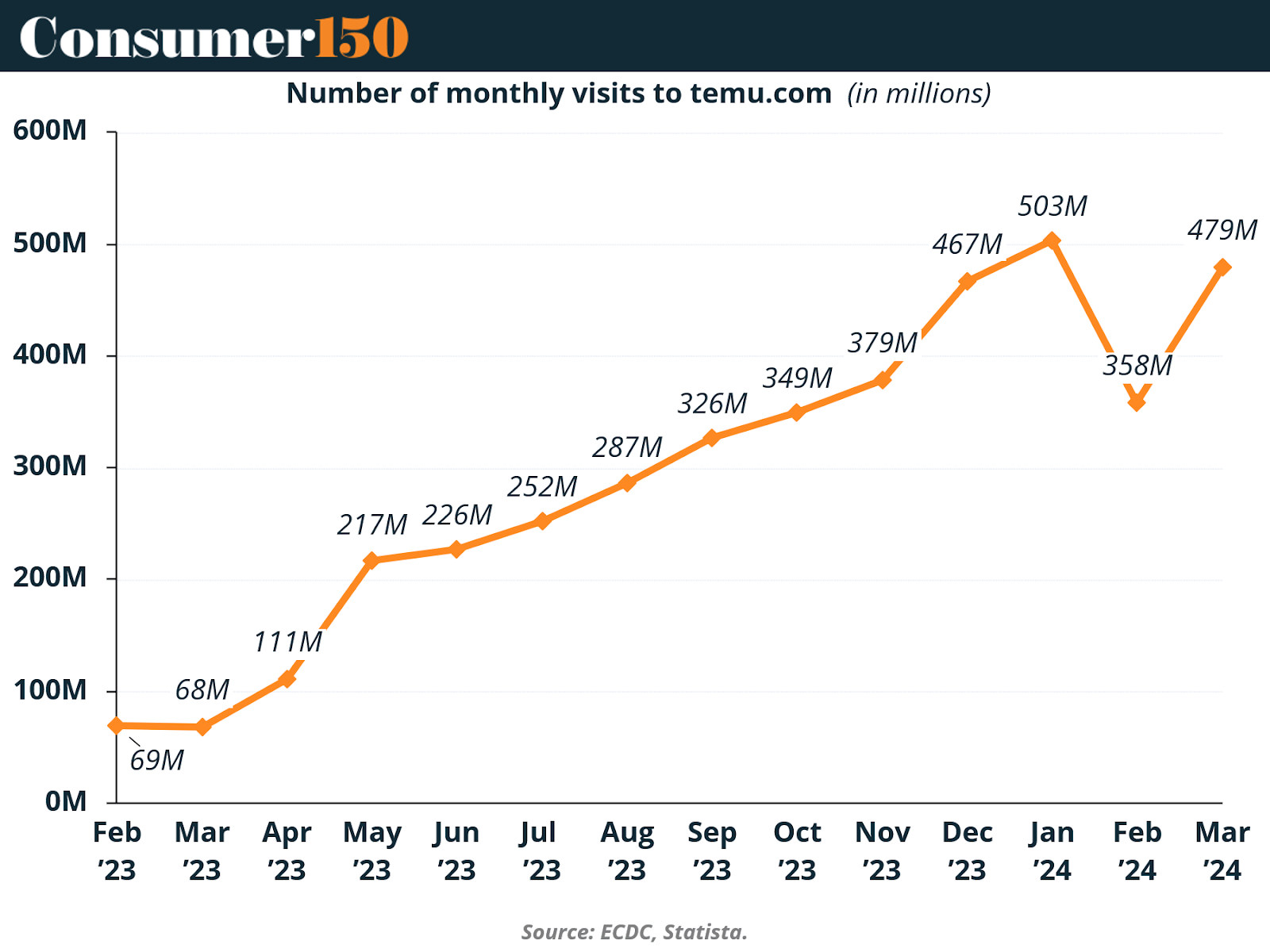
From February 2023 to March 2024, monthly visits to Temu.com grew from just 69 million to nearly 500 million, with peaks exceeding half a billion in early 2024. Even after seasonal dips, the platform quickly rebounded, underscoring its strong consumer stickiness. The data suggests that Temu’s initial novelty factor has evolved into sustained usage—a rare feat for a platform so reliant on discount-driven marketing.
Temu’s geographic footprint also provides insight into its long-term strategy.
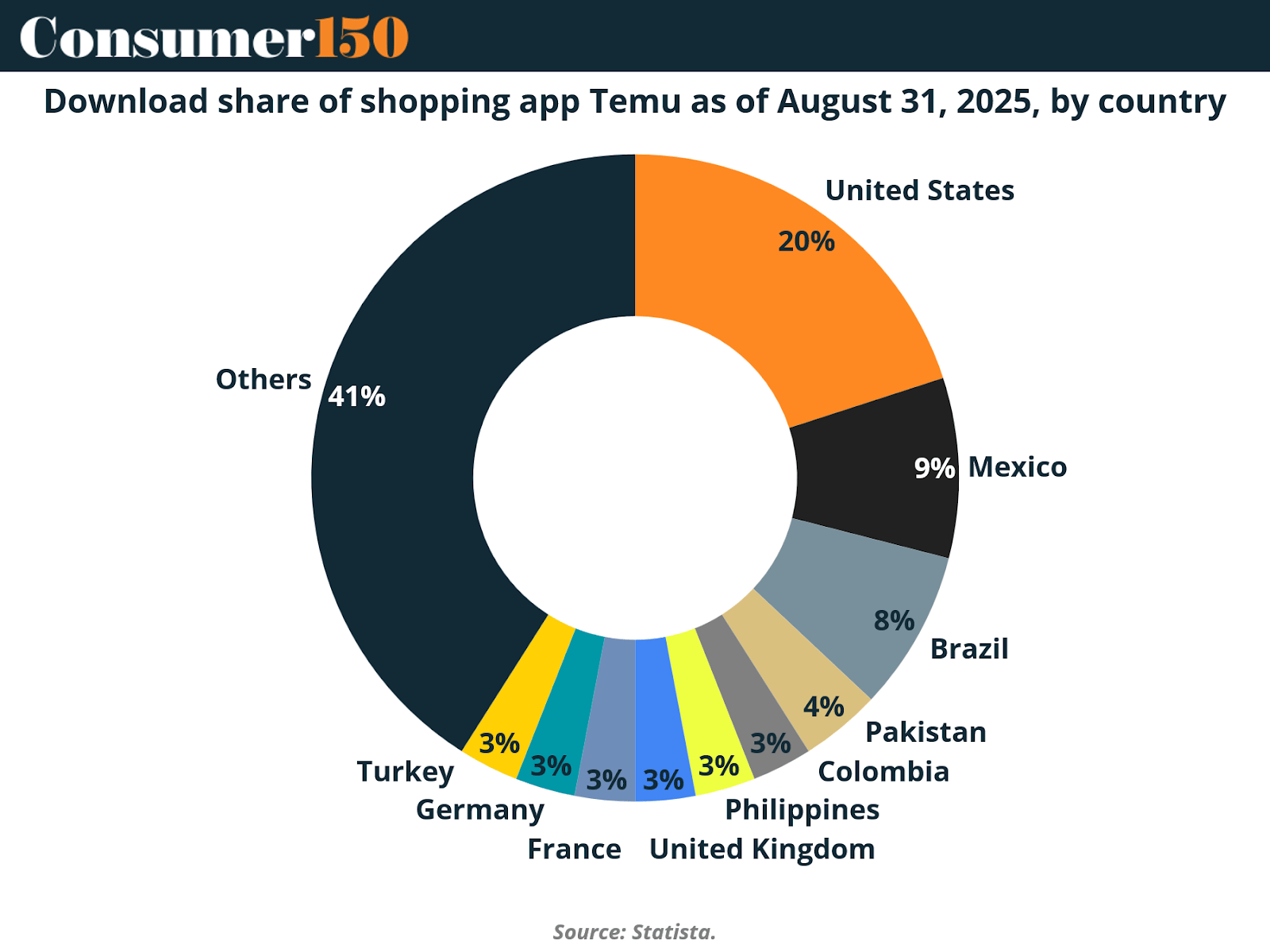
The United States accounts for 20% of global downloads, followed by Mexico (9%) and Brazil (8%). The remaining 41% comes from a mix of emerging markets and smaller economies, showing Temu’s diversification beyond Western consumers. The company’s expansion into Latin America, Europe, and Southeast Asia highlights its ambition to build a multi-regional ecosystem, using low-cost shipping and localized marketing to penetrate new demographics.
One of Temu’s greatest advantages lies in its data-driven manufacturing model. Unlike Amazon, which acts largely as a marketplace for existing products, Temu leverages real-time data from search trends, click rates, and purchase patterns to guide Chinese manufacturers on what to produce. In exchange for this data, factories offer Temu steep discounts, creating a feedback loop that minimizes risk and optimizes demand forecasting. This approach drastically shortens the product cycle—from design to sale—allowing Temu to constantly refresh its catalog with items that align precisely with user interests.
Temu’s brand identity also plays a key role in its disruption. Its marketing message—“Shop like a billionaire”—taps into aspirational consumer psychology, presenting luxury through affordability. The company’s viral Super Bowl campaigns, costing tens of millions of dollars, cemented Temu as a household name in the U.S. Almost immediately after its commercials aired, Temu’s downloads spiked, while Amazon and eBay saw brief declines in web traffic. Through strategic use of short-form video, influencer partnerships, and algorithmic advertising, Temu has managed to turn shopping into entertainment—merging social media and retail into one frictionless experience.
Yet behind this success lies a controversial undercurrent. Temu has faced repeated accusations regarding labor practices and supply chain ethics. Reports from U.S. and U.K. politicians have raised concerns about forced labor in its supplier networks, particularly in China’s Xinjiang region. Temu has denied these allegations, stating that it “strictly prohibits” any form of forced, penal, or child labor, and that all merchants must comply with local labor laws. Still, regulatory scrutiny persists, especially as geopolitical tensions rise between China and Western governments.
The eCommerce Industry and Tariffs Impact
Temu’s global strategy cannot be understood in isolation—it is deeply intertwined with the broader evolution of the eCommerce industry and the geopolitical shifts shaping global trade.
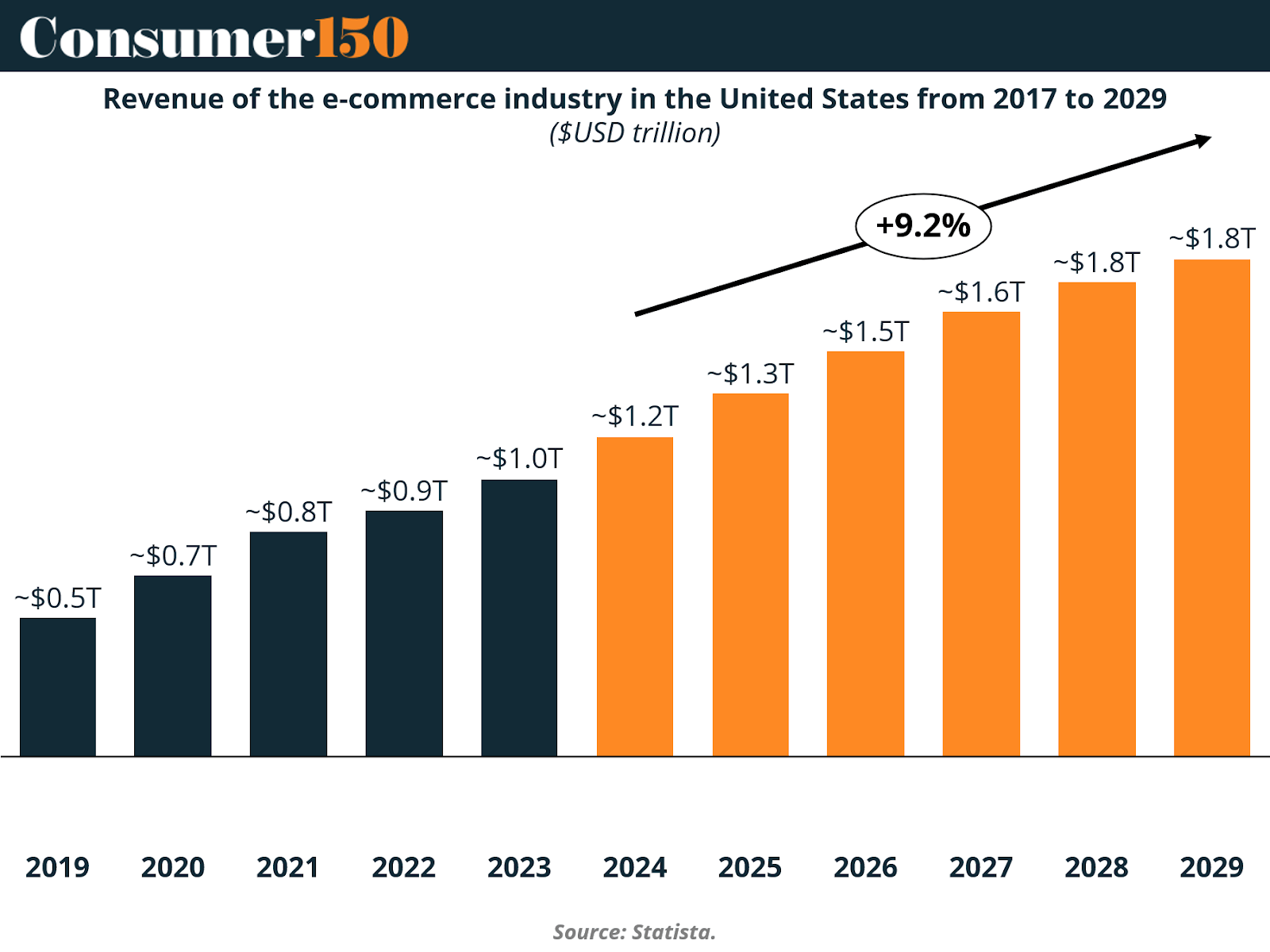
The U.S. eCommerce market has grown steadily, reaching approximately $1.2 trillion in 2024 and projected to surpass $1.8 trillion by 2029. This consistent expansion provides fertile ground for players like Temu to capture new segments of digital consumption. However, Temu’s reliance on China’s manufacturing base places it in a precarious position amid shifting tariff policies.
In 2025, under renewed trade measures by President Donald Trump, the U.S. reintroduced high tariffs on imported goods from China, directly affecting platforms like Temu and Shein. Temu’s business model, heavily dependent on Chinese production and cross-border logistics, faces mounting pressure as shipping costs and import taxes rise.
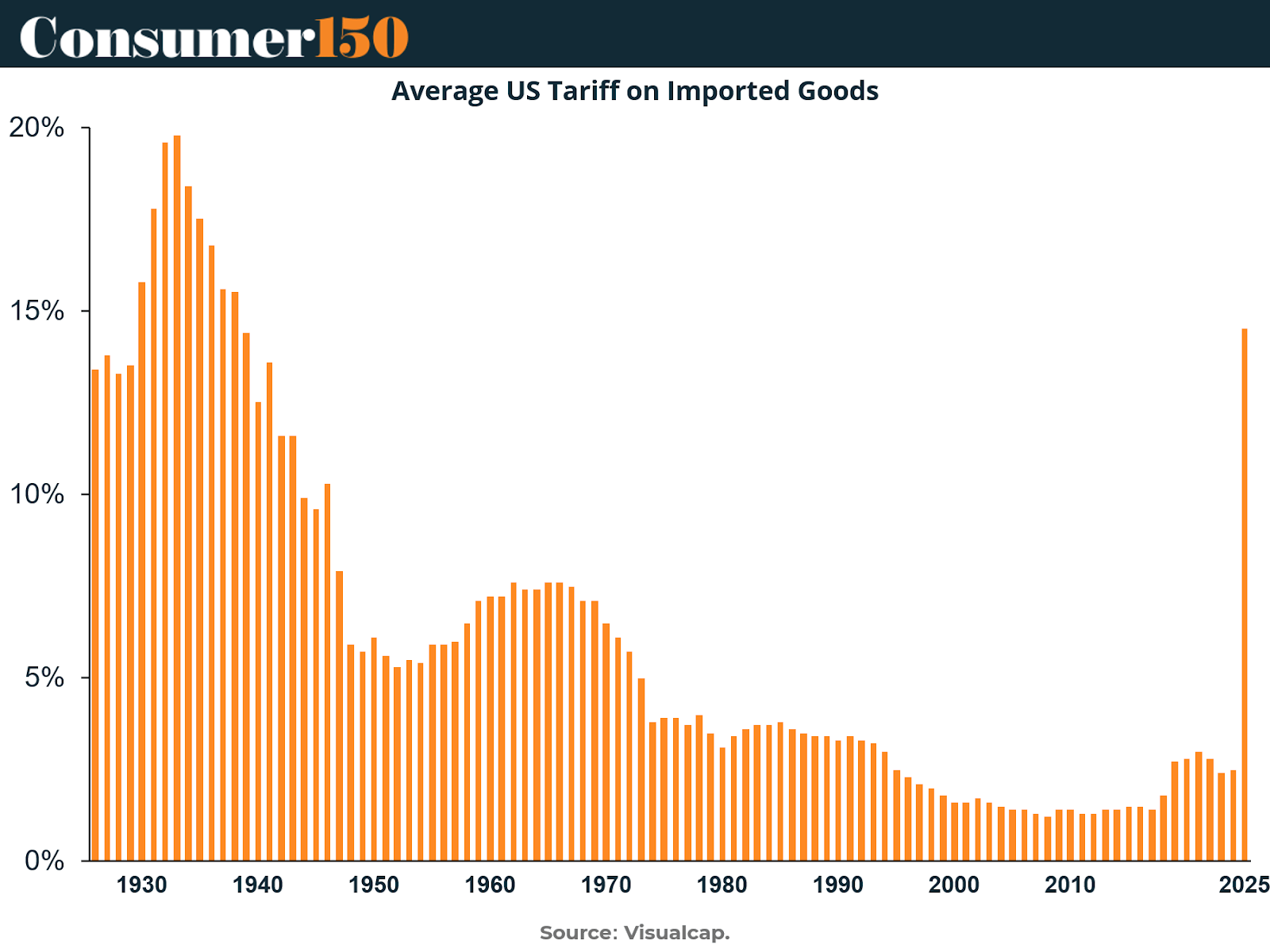
After decades of declining tariffs, 2025 marked a sharp resurgence, with average import duties jumping to levels not seen in decades. For eCommerce platforms like Temu, which rely on thin margins and ultra-low prices, this poses a direct threat to competitiveness.
To mitigate these challenges, Temu has started promoting U.S.-warehoused products and partnering with local sellers. This hybrid model aims to reduce exposure to tariffs while maintaining its core promise of affordability. By investing in logistics hubs and warehousing, Temu hopes to recreate its Chinese efficiency within the American ecosystem—an ambitious effort that could either cement its long-term viability or erode its cost advantage.
The policy backdrop is especially relevant given projections of eCommerce market trajectories under different tariff scenarios.
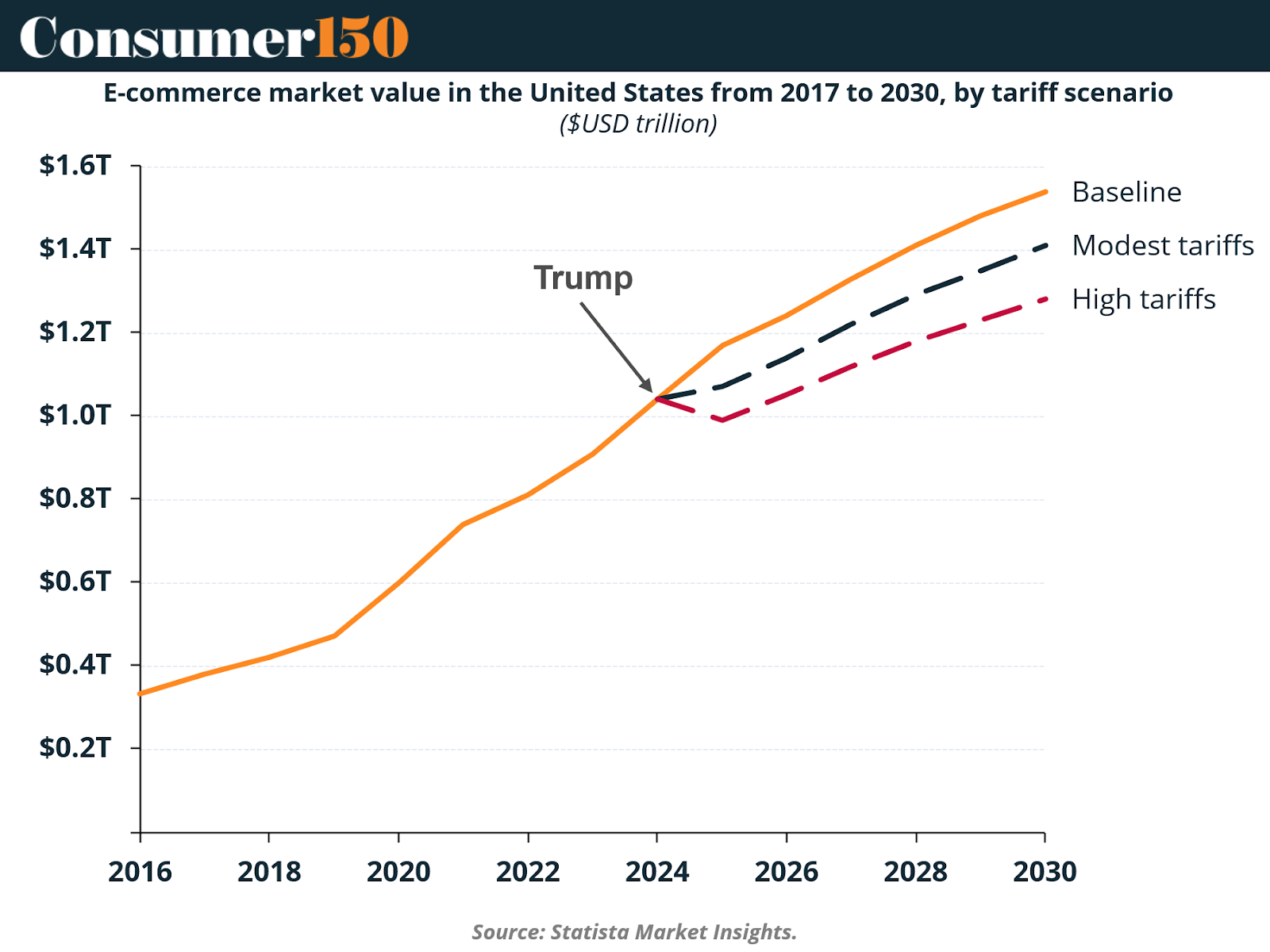
Under baseline conditions, U.S. eCommerce was projected to continue its upward path beyond $1.5 trillion by 2030. However, under modest tariff scenarios, growth decelerates, while high tariffs could cut the sector’s expansion by nearly a third. These pressures disproportionately affect foreign-based platforms like Temu, which depend on imports for the majority of their product catalog.
Temu’s reaction to tariffs showcases its adaptability. The company is shifting toward a “fully managed” retail model, in which it takes greater control over pricing, product selection, and logistics. This shift echoes Amazon’s early vertical integration strategy and signals Temu’s intent to evolve from a simple marketplace into a comprehensive retail ecosystem. PDD’s investment in merchant support programs—spanning billions of dollars—illustrates the depth of this commitment.
At the same time, the company faces intensified competition both domestically and internationally. In China, Pinduoduo competes fiercely with Alibaba and JD.com, while overseas Temu must contend with Amazon, Walmart, and a rising wave of regional players such as MercadoLibre in Latin America and Shopee in Southeast Asia. The ensuing price wars are squeezing margins across the industry. As PDD executives noted, industry competition has intensified significantly, and the company does not consider its current profit levels sustainable.
Temu’s situation reflects a broader transformation of eCommerce economics: the pivot from growth at all costs to sustainable profitability. The company’s model—anchored in low-cost production, free shipping, and aggressive advertising—faces a future where operational efficiency and compliance may matter as much as virality.
However, Temu’s ability to maintain high engagement and long browsing times suggests that its brand loyalty is resilient even amid cost pressures. Moreover, the platform’s demographic diversity further strengthens its potential for longevity.
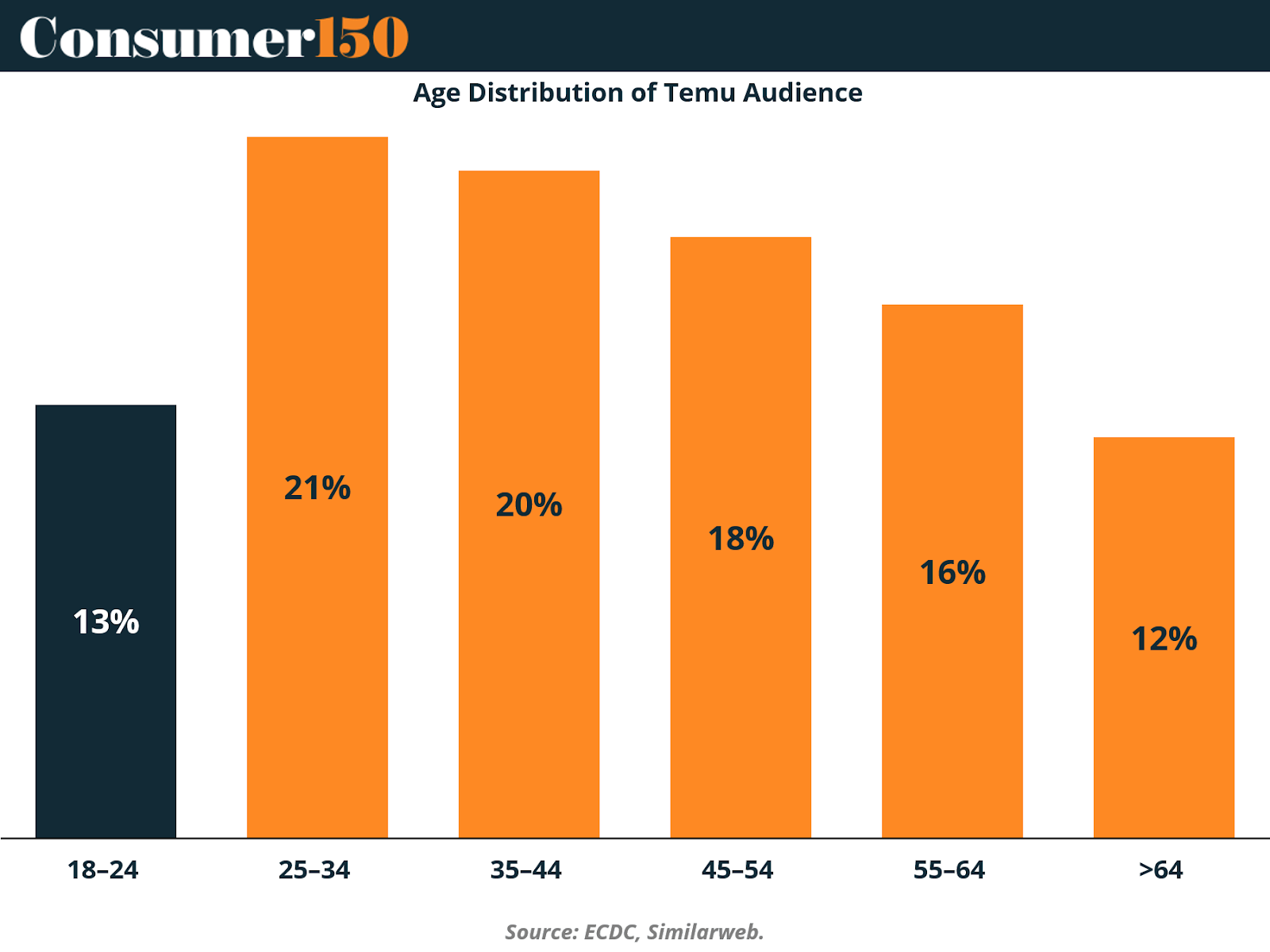
Temu’s user base is surprisingly mature: only 13% of users are aged 18–24, while the 25–54 demographic makes up nearly 60% of its total audience. This distribution contrasts sharply with rivals like Shein or TikTok Shop, which depend heavily on younger consumers. By appealing to a more balanced age mix—one that includes middle-aged buyers with greater disposable income—Temu is building a more stable foundation for long-term growth.
This broad appeal is particularly evident in markets such as the U.S., where inflationary pressures have pushed consumers toward discount-driven platforms. Temu’s model of direct-from-factory pricing and gamified shopping resonates with price-conscious shoppers, especially those in suburban and rural regions underserved by traditional retail. The company’s integration with TikTok, YouTube, and Instagram micro-influencers amplifies its reach, tapping into the viral potential of social commerce.
At the same time, Temu’s heavy dependence on data collection has raised privacy and cybersecurity concerns. Analysts have noted that Temu’s data harvesting model—tracking consumer behavior to optimize product recommendations—is similar to that of its Chinese counterpart, Pinduoduo, which has faced periodic bans and investigations for data misuse. These concerns, while often politically amplified, highlight the tension between innovation and regulation that defines Temu’s global footprint.
In many ways, Temu’s disruption mirrors the early days of Amazon: relentless expansion, mounting losses, and a race to build infrastructure before regulation catches up. The difference is that Temu operates under a much more complex geopolitical landscape—one in which digital commerce has become a proxy for national economic rivalry.
Conclusion
Temu’s rise encapsulates the story of modern globalization—fast, digital, and politically charged. Within just three years, the company has transformed from a little-known Chinese export experiment into one of the world’s most influential eCommerce platforms. Its blend of affordability, entertainment, and data-driven manufacturing has altered consumer expectations and forced established giants like Amazon, Walmart, and eBay to reexamine their strategies.
Temu’s success stems from an intricate ecosystem powered by Chinese supply chains, AI-driven insights, and a viral marketing engine that thrives on social engagement. Yet, as its growth stabilizes and tariffs mount, the company faces the complex task of transitioning from a growth disruptor to a sustainable global enterprise. Its strategy of promoting U.S.-stored goods and engaging local sellers signals a pragmatic pivot toward regional integration, an acknowledgment that cross-border eCommerce cannot rely indefinitely on loopholes like the de minimis shipping threshold.
The broader implications of Temu’s disruption are far-reaching. Economically, it challenges the assumption that scale and longevity are prerequisites for dominance in retail. Politically, it illustrates how trade policy can shape the digital economy. Socially, it exposes consumers’ shifting priorities—from brand loyalty to price efficiency, from convenience to digital immersion.
Despite controversies surrounding labor practices and data collection, Temu’s influence is undeniable. It has democratized access to goods in an era of economic uncertainty, offering consumers a digital bazaar of affordability at a global scale. Whether it can sustain this momentum under the weight of tariffs, competition, and regulatory scrutiny remains uncertain—but its impact has already redrawn the map of global retail.
Temu’s future will likely hinge on balance: between cost and compliance, innovation and oversight, global reach and local relevance. If it manages to strike that equilibrium, the “Amazon on steroids” label may soon evolve into something even larger—a blueprint for the next generation of borderless, data-driven commerce.
Sources & References
BBC. (2024). How Temu is shaking up the world of online shopping. https://www.bbc.com/news/business-68563339
ECDB. (2024). Temu Business Model 2024: Gaming, Gambling & Low Prices. https://ecdb.com/blog/temus-strategy-to-compete-in-the-realm-of-ultra-fast-ecommerce/4439
Reuters. (2025). Temu-owner PDD tops revenue estimates, competition squeezes margins. https://www.reuters.com/world/china/temu-owner-pdd-tops-revenue-estimates-competition-squeezes-margins-2025-08-25/
Statista. (2025). Download share of shopping app Temu as of August 31, 2025, by country. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1399990/temu-country-share-of-app-downloads-worldwide/
Statista. (2025). Leading online marketplaces worldwide in 2024, by gross merchandise value. https://www.statista.com/forecasts/1456497/top-online-fashion-marketplaces-by-gmv
Statista. (2025). Number of global downloads of shopping app Temu from September 2022 to August 2025. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1393504/temu-number-of-app-downloads-worldwide/
Statista. (2025). Number of monthly visits to temu.com from February to May 2025. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1466133/number-visits-temu-website/
Premium Perks
Since you are an Executive Subscriber, you get access to all the full length reports our research team makes every week. Interested in learning all the hard data behind the article? If so, this report is just for you.
|
Want to check the other reports? Access the Report Repository here.
