- Consumer 150
- Posts
- Consumers Lean Local Over Global: A New Era of Purchase Priorities
Consumers Lean Local Over Global: A New Era of Purchase Priorities
In recent years, consumer sentiment has been gradually shifting away from multinational giants toward homegrown, locally owned brands.

By 2025, this shift has solidified into a global trend, reshaping how brands compete in both established and emerging markets. While affordability and familiarity still play a role in consumer decision-making, supporting local businesses and aligning with domestic values have emerged as defining motivations.
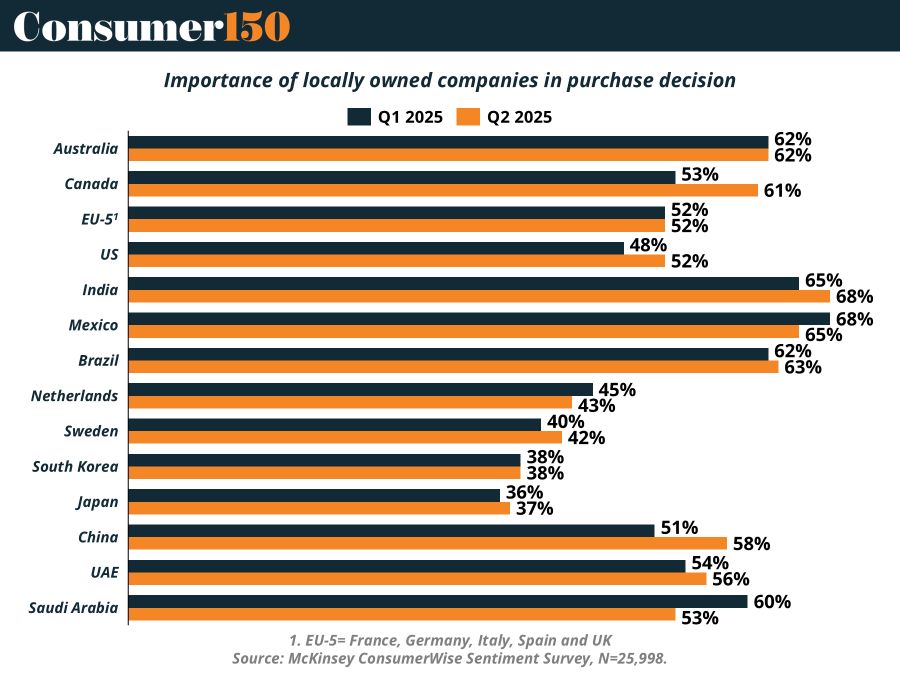
According to the latest McKinsey ConsumerWise Sentiment Survey (Q2 2025), 47 percent of global consumers now say that whether a company is locally owned plays a key role in their purchase decision. This preference is especially pronounced in countries like Mexico (68%), India (68%), Brazil (65%), and Canada (61%), each showing a substantial share of consumers prioritizing local ownership when buying.
The trend isn't limited to emerging markets. Canada and the United States have seen some of the most significant quarter-over-quarter increases, with Canada rising from 53% in Q1 to 61% in Q2 2025, and the U.S. jumping from 48% to 52% in the same period. This reflects a broader North American recalibration of brand trust, identity, and loyalty—one influenced not just by economics but also by shifting trade dynamics and cultural resonance.
What’s Driving the Shift Toward Local Brands?
The motivations behind this trend are as much emotional as they are rational. When asked why they prefer local brands:
36% of global consumers said they want to support domestic businesses, highlighting a sense of civic or national responsibility.
20% said that local brands better fit their needs, suggesting that customization and cultural relevance are winning attributes.
Only 13% cited affordability, signaling that price is not the primary factor driving the turn toward local products.
This preference for local is particularly visible in specific product categories such as apparel, food, and household goods, where consumer-brand relationships are strongest and most personal. In Japan, 9 of the top 10 snack brands are domestic, and in China, 6 of the 10 fastest-growing beauty brands since 2020 are Chinese—up from just two in the previous five-year period.
Evolving Brand Perceptions and Global Implications
Interestingly, the trend is also marked by a shifting perception of foreign—particularly American—brands. In Europe, 42% of consumers report a declining perception of U.S. brands compared to earlier in the year, suggesting growing skepticism about the relevance, values, or behavior of certain multinational companies.
As trade landscapes evolve and economic nationalism gains ground in many regions, multinational companies face higher expectations and greater scrutiny when expanding into foreign markets. The growing appetite for local alternatives places pressure on global players to reevaluate their localization strategies. Simply having a global footprint is no longer a competitive advantage unless it is backed by tangible local impact.
Strategic Implications for Global Brands
Looking forward, winning in local markets will require more than distribution—it will demand authentic presence, localized product development, and cultural fluency. Brands must tailor offerings to local needs, adapt messaging and packaging, and where feasible, even localize their supply chains. Those unable to do so may need to rethink their global ambitions and double down on core markets, especially amid the uncertainties of new trade agreements and geopolitical friction.
For legacy players and disruptors alike, the message is clear: local matters more than ever. The brands that thrive will be those that can strike a balance between global scale and local authenticity—delivering not just products, but a sense of place and purpose that resonates with the consumer.